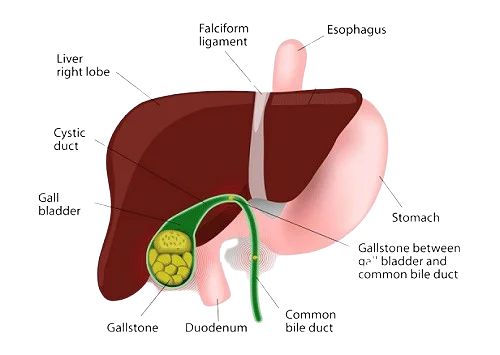
Gall Bladder & Bile Duct Stones
Treatments
Gall Bladder & Bile Duct Stones
Gallbladder and bile duct stones are common medical conditions related to the biliary system, which plays a crucial role in digestion. Here's a detailed overview:
1) Gallbladder Stones (Cholelithiasis)
Definition:
Gallbladder stones, also known as cholelithiasis, are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in the gallbladder.
Symptoms

Biliary Colic
Intense abdominal pain, typically in the upper right part of the abdomen, often after a meal.

Nausea and Vomiting
These symptoms may accompany biliary colic.
Jaundice
If a stone obstructs the bile duct, it can cause jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Fever and Chills
These symptoms may indicate complications such as cholecystitis or cholangitis.
Diagnosis
Ultrasound:
The most common imaging test used to diagnose gallstones.
CT Scan or MRI:
These may be used if the ultrasound results are inconclusive.
Blood Tests:
Elevated levels of bilirubin or liver enzymes may suggest a blockage or inflammation.
Treatment

Watchful Waiting
Asymptomatic gallstones may not require treatment.

Medications
Ursodeoxycholic acid can help dissolve certain types of gallstones.

Surgery
Cholecystectomy, the surgical removal of the gallbladder, is the most common treatment for symptomatic gallstones.
Causes
Imbalance in Bile Components:
Imbalance in the constituents of bile, such as cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin, can lead to stone formation.
Stasis of Bile:
When bile remains in the gallbladder for an extended period, it can become concentrated and form stones.
Genetic Factors:
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gallstone formation.
Obesity:
Obesity is a risk factor for developing gallstones.
Rapid Weight Loss:
Quick weight loss can increase the risk of gallstone formation.
Certain Medications:
Some medications can increase cholesterol levels in bile, contributing to stone formation.
2) Bile Duct Stones (Choledocholithiasis)
Definition:
Bile duct stones are gallstones that have migrated from the gallbladder into the bile ducts.
Symptoms

Similar to Gallbladder Stones
Biliary colic, jaundice, fever, nausea, and vomiting.

Complications
Choledocholithiasis can lead to more severe complications like cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts) or pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
Diagnosis
Imaging:
Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, or MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) to visualize the bile ducts.
Endoscopic Procedures:
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) allows for both diagnosis and treatment by removing stones from the bile ducts.
Treatment

Endoscopic Removal
ERCP with sphincterotomy and stone extraction is the primary treatment for bile duct stones.

Surgery
In some cases, surgical removal of the stones may be necessary, especially if ERCP is not feasible or successful.
Causes
Migration from Gallbladder:
Gallstones can move from the gallbladder into the bile ducts, causing obstruction.
Primary Bile Duct Stones:
In some cases, stones can form directly within the bile ducts.

