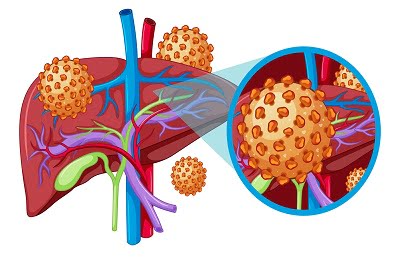
Acute Viral Hepatitis

Hepatitis A (HAV)
Transmitted primarily through ingestion of contaminated food or water or through close contact with an infected person. It usually resolves on its own and doesn't cause long-term liver damage.

Hepatitis B (HBV)
Transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or other body fluids. It can be acute or chronic. Acute HBV infection may resolve on its own, but chronic HBV can lead to serious liver problems such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Hepatitis C (HCV)
Primarily spread through blood-to-blood contact. Like HBV, HCV infection can be acute or chronic. Acute HCV infection often goes unnoticed, but chronic infection can lead to liver damage over time.

Hepatitis D (HDV)
This virus only infects those who are already infected with HBV. HDV can worsen the symptoms of HBV infection and lead to a more severe form of hepatitis.

Hepatitis E (HEV)
Commonly transmitted through contaminated water in developing countries. It's usually self-limiting, but it can be dangerous for pregnant women, leading to acute liver failure.