Endoscopy
Technology
Endoscopy
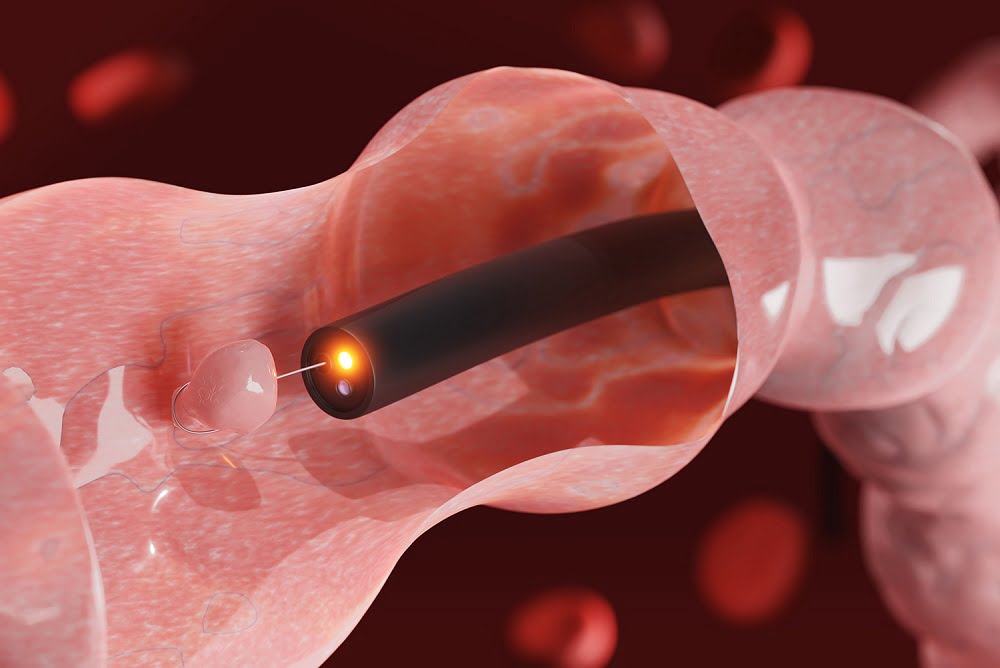
Introduction
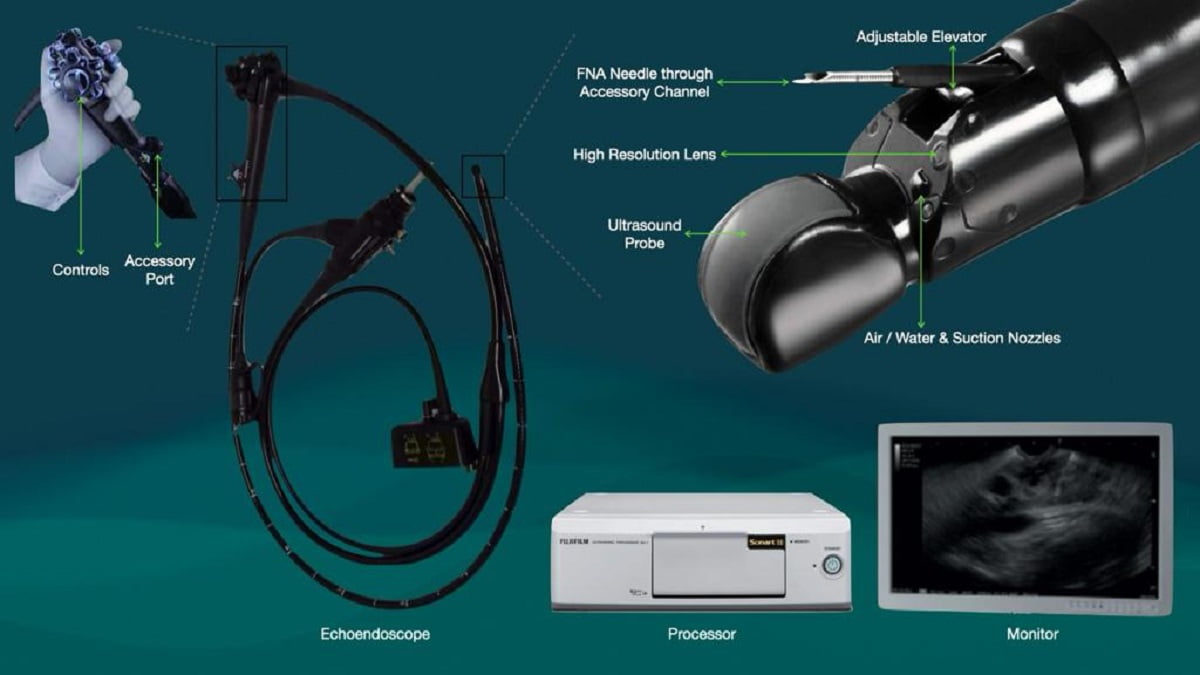
Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS)
- Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) pairs the technology of endoscope and high frequency ultrasound waves from a transducer placed at the distal tip of the echo endoscope.
- It is used to visualise gastrointestinal walls and adjacent structures, for cancerous lesions and diseases of mediastinum, abdomen and pelvis.
- Esophagus, stomach, duodenum, colon, rectum, mediastinum, celiac plexus, liver, gall bladder, hepato-biliary tree, portal venous system, pancreas, mediastinal & abdominal major arteries & veins, mediastinal & abdominal lymph nodes are some of the structures that can be studied with greater detail on EUS.
- Greek origin word
- Endo = Inside
- Skopeein = To see
- Examination of the interior of a hollow viscus or canal by a special instrument
- First fiberoptic endoscope by Basil Hirschowitz in 1958
- Stone in biliary tract
- Cholangitis
- Biliary strictures (Benign / Malignant)
- Biliary leak
- Pancreatic stones
- Pancreatic strictures
- Pancreatic leak
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography (ERCP)
Liver & Biliary Tree
Mediastinum
Ampulla
Wall Evaluation
Pancreas
Pancreatic Fluid Collections
Liver Elastography
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography (ERCP)
[elementor-template id=”16581″]
Liver & Biliary Tree
[elementor-template id=”16600″]
Mediastinum
[elementor-template id=”16597″]
Ampulla
[elementor-template id=”16594″]
Wall Evaluation
[elementor-template id=”16590″]
Pancreas
[elementor-template id=”16587″]
Pancreatic Fluid Collections
[elementor-template id=”16584″]
Liver Elastography
[elementor-template id=”20608″]


